America’s Best
Paystub Generator
A paystub generator built for business owners, entrepreneurs, and employees paid in cash.
Based on Google Reviews

- Employee Pay Stub for Income Verification
- Pay Stub for Payroll Management
- Pay Stub for Tax Filing
- Pay Stub for Loan Applications
- Pay Stub for Employment Verification
- Employee Pay Stub for Benefits Enrollment
- Pay Stub for Unemployment Claims
- Paystub for Self Employed/Freelancers
- Paystub for Small Businesses
- Paystub for Buying a House
- Paystub for Drivers & Dispatchers
- Paystub for Independent Contractors
- Paystub for Disability
- Paystub for Visa Application
Partner with more than 100+ big companies






What is a Pay stub?
A pay stub is a document that summarizes an employee’s pay for a specific pay period. It’s typically created by an employer in conjunction with each paycheck and can be provided in paper or electronic form. Pay stubs are also known as paycheck stubs, check stubs, earnings statements, or pay slips.
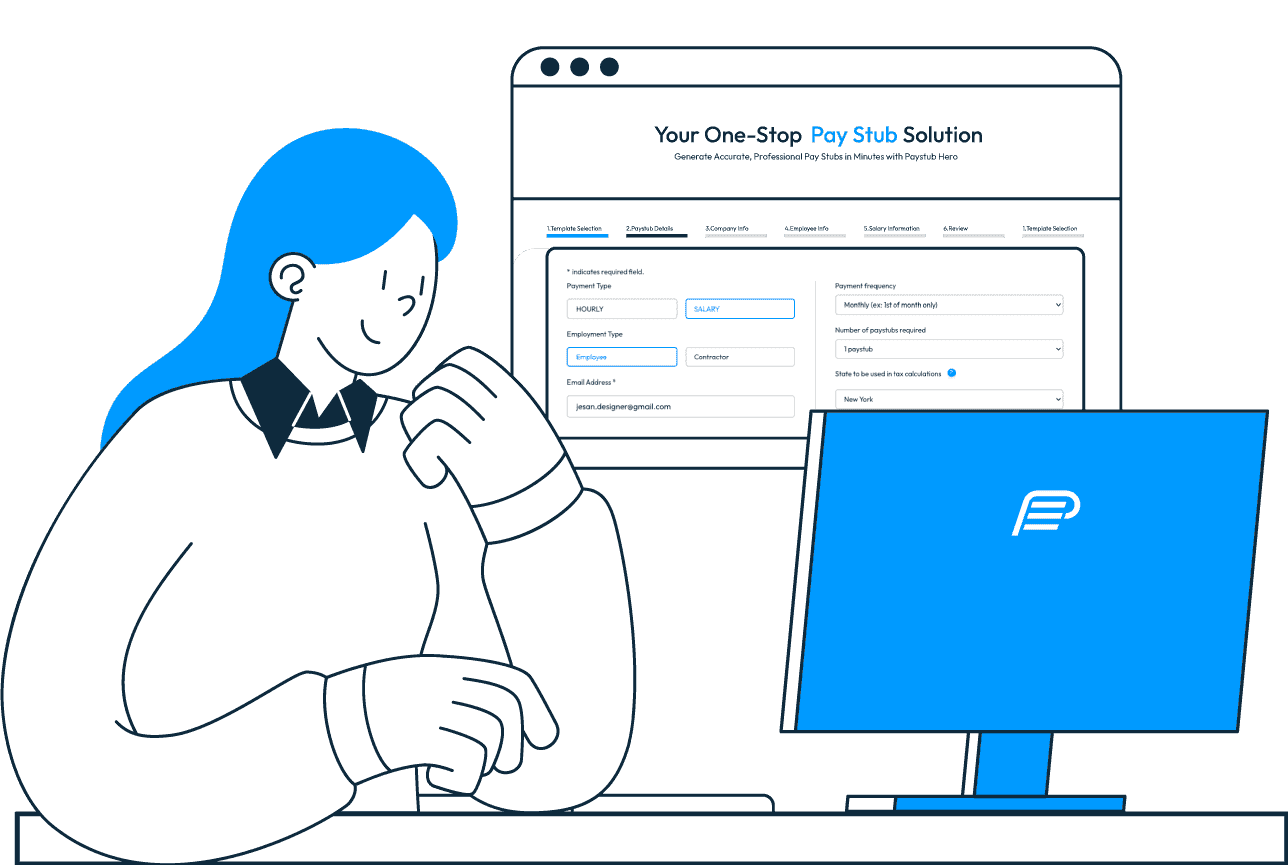
Our paystub generator has your income verification needs.
PaystubHero provides a wide selection of paystub templates to suit your needs. Whether you’re looking for designs inspired by ADP paystubs or prefer sleek, modern styles, we’ve got you covered!


Best Pay Stub Generator
$7.50
/ Per Paystub
Unbeatable Value at Just Only $7.50
- 100% Accurate Calculations
- 24/7 Customer Support
- Transparent Pricing
- Highly Customizable
- Fully Compliant
We offer the Best Pricing in The paystub generator industry
Transparent Pricing, Unmatched Value – That’s the Paystub Hero Promise
How PaystubHero Makes Pay Stubs Instantly
With PaystubHero, you can instantly create accurate paycheck stubs for any situation. Our platform simplifies the process, offering customized pay stubs ready for use in minutes. Choose from PDF or other digital file types for fast, secure download.
Whether you need detailed pay stubs or proof of income, PaystubHero makes it quick and easy to create accurate and reliable paycheck documentation anytime.
Steps to use our Check Stub Maker
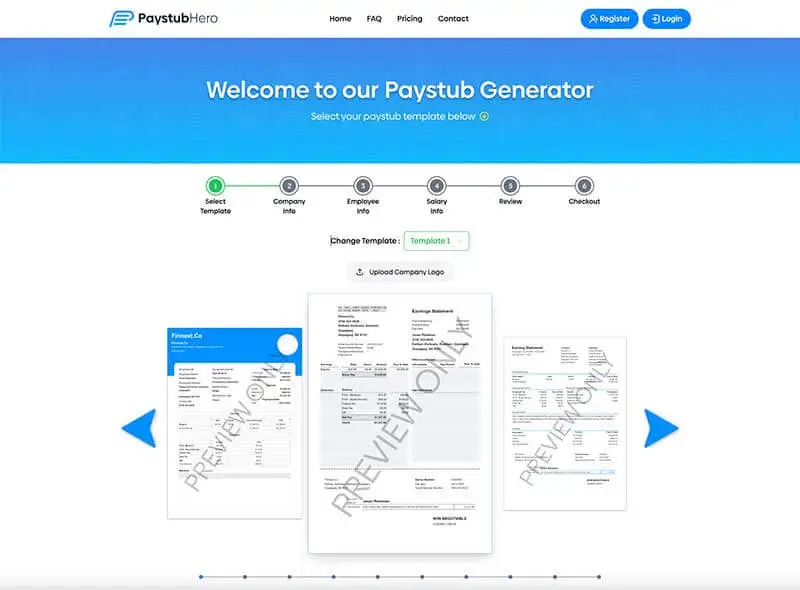
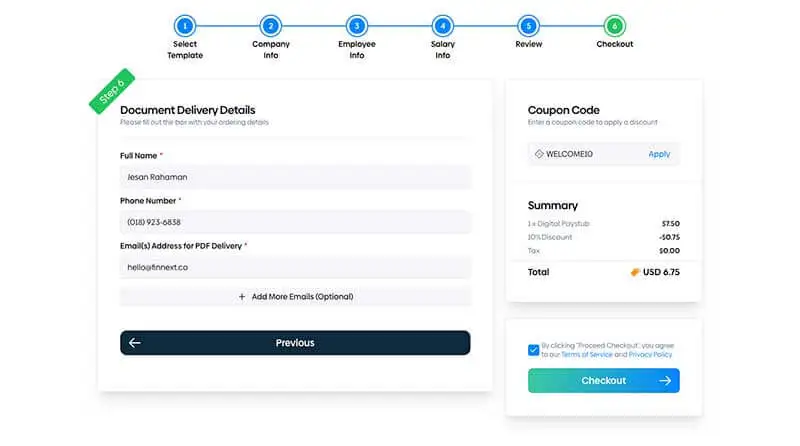
Choose a pay stub template from our 10 designs
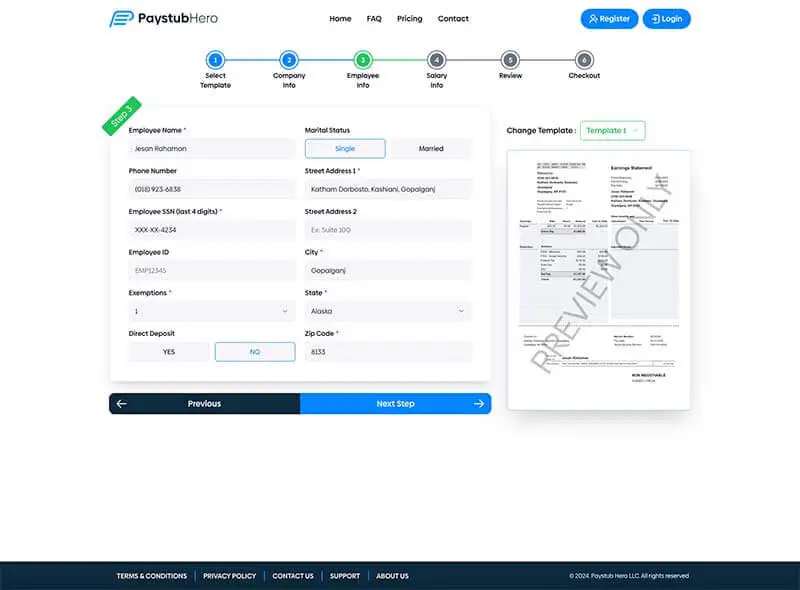
Enter Information such as company name, your work schedule and salary details
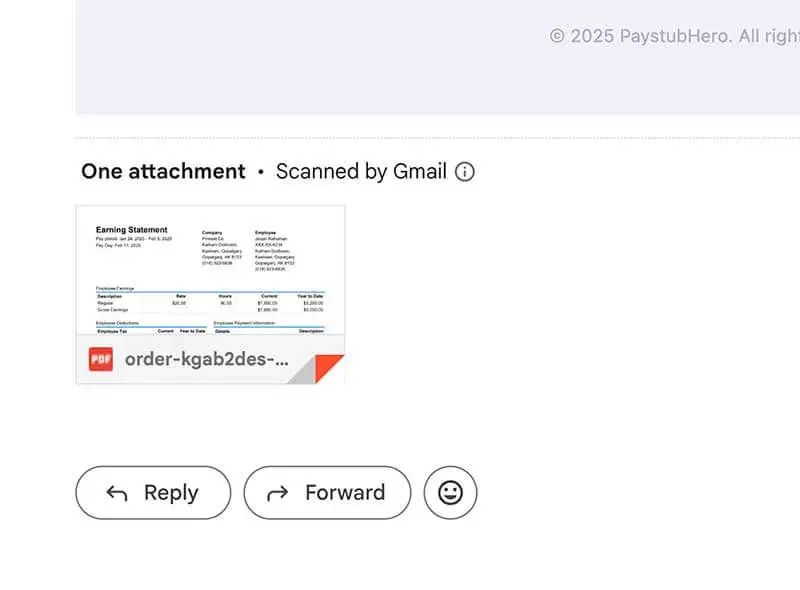
Download your paycheck stubs directly from your email in PDF format
Why choose our Paystub generator vs. others
Our paystub generator, unlike any other online paystub maker, is problem free. In less than two minutes, you can complete your pay stub by simply entering your company name and salary details. Our efficient pay stub calculator software makes it quick and easy for you to get professional results.
- Lightning-Fast Paystub Generation
- Top-Notch Customer Support
Personal Profile
Where you can download all your old document

10% Off First Time
Use coupon code: WELCOME10
We've Helped 839,492 Customers Create Their Paystub Template Using Our Stub Generator





Experience the PaystubHero Advantage
Enjoy Unparalleled Benefits with Our Pay Stub Generator
People also ask
Whether through Google, ChatGPT, or PaystubHero live chat, here are frequently asked questions people ask about Paystubs.

How do you read a paystub?
A paystub is a simple breakdown of your earnings for a given pay period. It shows your gross pay, which is the total you earned before any deductions, and lists things like taxes, and insurance.
After all the deductions, you’ll see your net pay. The amount you actually take home.
Pay stubs also include details like:
- The dates of the pay period
- Your name
- Your employer’s info.
It’s basically a summary of your paycheck, helping you understand where your money’s going.
Types of Deductions on a Paystub
A paycheck stub has several deductions, but there are a few major ones you’ll always see. Below is a quick look at the key deductions on a paystub:
Federal Tax Withholding
The federal tax withholding is the amount taken out for federal income tax. It’s based on how much you earn and your tax situation. This deduction helps fund important government programs like education, defense, and infrastructure.
The more you earn, the more federal tax will be taken.
State Tax Withholding
State tax withholding is similar to federal tax, but it’s for your state government.
Depending on where you live, this can vary a lot. Some states, like Florida or Texas, don’t have a state income tax at all. But if you live in a state that does, a portion of your paycheck will go to fund local programs like schools, roads, and public services.
The amount depends on your income and your state’s tax rate.
Social Security Tax
Social Security tax is another mandatory deduction that helps fund the Social Security program, which provides benefits to retirees and people with disabilities.
The rate for Social Security tax is 6.2% of your income.
This tax ensures that when you retire, or if you’re unable to work due to a disability, you have some financial support.
Medicare Tax
Medicare tax is the amount taken out to fund Medicare, which provides healthcare benefits for people aged 65 and older.
The standard rate for this deduction is 1.45% of your income, and there’s no cap on how much can be taxed. For higher earners, there’s an additional 0.9% tax.
This helps ensure that when you’re older, you’ll have access to necessary medical services.
Health Insurance Premium
If your employer offers health insurance, this deduction covers the cost of your plan.
Depending on your plan, the amount can vary. It’s often taken out before taxes, which helps reduce your taxable income. Having health insurance is important to cover medical expenses, like doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescriptions.
The exact amount depends on the type of coverage you choose, whether it’s just for you or for your whole family.
Retirement Contributions
Retirement contributions are deductions for savings that go toward your future.
If you have a 401(k) or similar retirement plan, a portion of your paycheck will go into that account. Some employers even match your contributions, which helps you save even more.
This is a great way to make sure you’re financially prepared when you retire. Plus, these contributions are often taken before taxes, lowering your taxable income now.
Types of Paystubs
Paystubs generally fall into two formats, but within these formats, the way earnings are structured also affects how a check stub looks. Let’s break it down.
Paper Pay Stubs vs Digital Pay Stubs
Paystubs can either be printed or digital.
Paper pay stubs are physical copies that come with a paycheck or are given separately for records. Some companies still use them, but most are switching to digital paystubs.
A digital paystub is an electronic version of a traditional paystub, stored online or emailed.
Benefits of Digital Paystubs vs Paper Pay Stubs
Digital paystubs offer some real advantages over traditional paper ones.
- Convenience and Accessibility
Have a think, how many times have you scrambled to find a paystub when you needed it?
Digital paystubs solve that.
They’re accessible anytime, anywhere, from your phone, tablet, or computer. You just log in or check your email. In fact, a report finds that 62% of employees prefer checking their paystubs digitally because it’s fast and convenient.
This eliminates the stress of digging through paper files. Everything’s at your fingertips.
- Better Organization and Record-Keeping
This ties in with the convenience.
Digital pay stubs are automatically stored and organized, making tax time so much easier. No more going through piles of paper. You can quickly search for specific pay periods or download a year’s worth of stubs in a few clicks.
Plus, digital records are less prone to errors than handwritten or manually filed ones.
- Environmental Impact and Cost Savings:
This is a big one.
Going digital reduces paper consumption, which is good for the planet. Think of all the trees saved. This is a well-established fact that reducing paper use has a positive environmental impact.
And for businesses, less paper means lower costs for printing, postage, and storage.
It’s a win-win.
Now, no matter the format, all paystubs contain key details like gross pay, deductions, and net pay. The structure varies however, based on how someone is paid.
➼ Paystubs for Hourly Employees
For hourly workers, paystubs break down hourly rate, total hours worked, overtime (if any), and deductions. Since their hours change, their paycheck stub fluctuates each period.
Overtime is usually calculated at 1.5 times the regular hourly rate, so extra hours mean extra pay. Jobs in retail, restaurants, and part-time work often use this type of check stub.
But salaried paystubs follow a different structure.
➼ Salaried Paystubs/Employee Paystubs
Unlike hourly workers, salaried employees receive a fixed paycheck regardless of how many hours they work.
Their employee pay stub reflects their annual salary divided by the number of pay periods, plus deductions for taxes, health insurance, and retirement plans. Salaried check stubs, like those for other employees, stay consistent unless there are bonuses or commissions.
However, for contractors, paystubs look quite different.
➼ Contractor Pay Stubs
Independent contractors and freelancers don’t get traditional paystubs since they handle their own taxes.
However, payroll services can generate contractor check stubs that show gross earnings without deductions. Unlike employee pay stubs, these won’t include tax withholdings or benefits.
Contractors must set aside money for taxes themselves. Full-time employees, however, have deductions automatically handled.
Who Uses a Paystub?
Paystubs serve different purposes for different people:
Employees
Paystubs help employees track their earnings, deductions, and take-home pay.
When tax season comes around, these check stubs make filing returns easier. They also serve as proof of income when applying for loans or even negotiating a salary at a new job.
Employers
Businesses rely on paystubs to maintain accurate payroll records and comply with tax regulations. If an employee ever questions their wages, a paycheck stub provides clear details.
It also ensures that the company is following labor laws and keeping everything documented properly.
Landlords and lenders
Before approving a lease or loan, landlords and banks need to verify income. A paystub shows stable earnings.
This helps landlords and lender assess timely payments.
Government agencies
Paystubs are often required for tax audits, social benefit programs, and unemployment claims. They confirm reported income, tax withholdings, and overall financial status.
What Are Paystubs Used For?
The above group of people use paystubs for different purposes. Below is how they play an important role in everyday life.
Pay Stub for proof of income
Landlords and lenders often ask for proof of income to ensure you’re financially stable. A paystub for renting an apartment or a paystub for mortgage applications serves as solid proof of how much you earn.
It gives them the reassurance they need that you’ll be able to make timely payments.
Without it, proving your income could be difficult, but with a clear paystub, it’s all laid out in black and white.
Paystub for tax filing
Since your employer deducts taxes from your paycheck, your paystub breaks down exactly what was taken out. This helps ensure that when it comes time to file your taxes, everything matches up.
Plus, you can check if you’ve overpaid or underpaid, and potentially claim a refund.
Paystub for payroll disputes
Mistakes happen, right? Maybe you noticed you weren’t paid for all the hours you worked or there was an error in your deductions. That’s where your stub helps.
It clearly lists everything you’re supposed to have earned, along with deductions and contributions.
If something’s off, your paystub can help you resolve the issue quickly by providing concrete proof of what should’ve been paid.
Paystub for loan applications
Lenders rely on your paystubs to verify your income, ensuring you meet their criteria for loan approval. It’s also a great way to show them that you have a steady stream of income to make those monthly payments.
Without this proof, securing a loan can be much harder, but with paystubs, you’re on solid ground.
Paystub for financial planning
Managing money doesn’t have to be overwhelming if you use your paystubs as a tool for financial planning. They help you see exactly what you’re earning and what’s being taken out for taxes, insurance, and retirement savings.
This transparency makes budgeting easier and allows you to plan for things like savings, investments, and future expenses.
Paystub for social benefits
Paystubs for disability, paystubs for unemployment, or stubs for other social benefits all fall under the same category when applying for government assistance. If you’re applying for disability, or any other type of financial support, you’ll likely be asked for paystubs.
Government agencies use these documents to verify your income and determine your eligibility for various benefits.
Paystubs help establish your financial standing, ensuring you get the support you need.
Paystub for legal matters
Paystubs can also play a role in legal situations.
For example, in divorce or child support cases, paystubs are often used to prove income levels. This helps the court determine fair alimony or child support payments.
In these cases, paystubs give an official record of your earnings, which is important for making sure everyone is treated fairly.
So, while you may not always think about it, your paystub could play a big role in legal matters.
Paystub for new job verification
Starting a new job? Some employers may ask for your previous paystubs to verify your salary history. This helps them decide what salary to offer based on your past earnings and ensures that they’re offering you a fair rate.
It’s a simple step that helps both you and your potential employer come to an agreement on salary expectations.
Paystub for business records
Paystubs for employees, small business owners, and freelancers all play a crucial role in maintaining accurate business records.
These stubs help ensure financial clarity, and they’re necessary for managing business operations or securing financial support.
How to Get a Paystub
Getting a check stub happens in two common ways. Either your employer provides it, or you generate one yourself.
➼ Getting One from an Employer
If you’re a traditional employee, your employer typically provides paystubs along with your paycheck. Many companies issue them digitally through an online payroll system, while others hand out printed copies.
If you’re not receiving one, check with HR or payroll. They might have an employee portal where you can download paystubs anytime.
➼ Using a Paystub Generator
Not everyone gets paystubs handed to them, especially freelancers, or small business owners. If you fall into that category, a paystub generator is your best bet.
Just enter your income details, and you’ll get a clear breakdown of earnings, taxes, and deductions.
Pay Stub Generators:
What They Are & How They Work
A pay stub generator is an online tool that makes it easy to create professional check stubs in minutes. No need to wait on an employer or deal with complicated paperwork. As we said earlier, just enter your earnings, deductions, and hours worked, and the generator does the rest.
For the steps, it’s super easy. Just follow a few quick steps, and you’ll have a professional pay stub ready to download.
And that brings up a common question, are these pay stubs real or fake?
The truth is, fake paystubs are out there, but PaystubHero provides real, verifiable ones that get the job done.
Real Check Stubs vs Fake Paystubs
A real check stub is a legitimate document issued by your employer or generated through a reputable check stub maker using a professional and recognized paystub template.
On the other side, a fake paystub is created with misleading or completely false details. People sometimes use fake paystubs to look more financially stable than they are, which could lead to serious problems down the road.
Fake stubs are usually easy to spot once you know what to look for.
How to Spot Fake Paystubs
Now, you might be wondering, “How do I tell if a paystub is real or fake?” It’s a good question, and there are a few key things to keep in mind.
According to Snappt, fake paystubs often show up with errors like inconsistent fonts, unusual formatting, or missing contact details for the employer.
One major red flag?
If the income listed seems too high for the job or doesn’t match industry standards, it’s definitely worth questioning.
To avoid falling for one, always take the time to double-check the details and verify anything that seems off. Using a trusted paystub generator is key here, so you know you’re getting accurate, reliable documents every time. Our software can help you avoid all of those issues with our robust algorithms and application.
Legal Risks of Using Fake Pay Stubs
Using fake paystubs comes with serious legal risks. Here are some potential consequences:
- Fraud charges
- Termination of employment
- Legal action from lenders or landlords
- Loss of government benefits or criminal charges
You can easily avoid these mistakes by using our paystub generator to provide you with legitimate documentation.
How Paystub Generators Help Small Businesses
Cash flow problems cause 82% of small businesses to fail. The main reason? Poor money management. If you’re not careful, you could face the same issues.
So how can a check stub generator help?
Paystubs break down earnings and deductions, helping track expenses and manage finances. Instead of guessing where your money is going, you get a record of wages, taxes, and other deductions.
This helps you stay on top of payroll, control cash flow, and avoid financial surprises.
Payroll Strategies for Small Businesses
The importance we discussed above comes as a result of smart payroll strategies. The below strategies help streamline payroll with paystub generators:
➼ Automate Payroll
Set up an automated system to generate paystubs for your employees each pay period. This ensures consistency, reduces the risk of human error, and saves time.
Using a paystub generator can make payroll easier to manage and free up resources for other tasks.
➼ Maintain Accurate Tax Records
With a paystub generator like PaystubHero, you can easily store all your paystubs in one place.
All you have to do is create an account, and every time you generate a new paystub, it’s saved for you. So, when tax season rolls around, you just log in, grab the records you need, and you’re good to go.
It’s a simple way to stay organized, make sure everything’s accurate.
➼ Offer Direct Deposit with Paystubs
Implement a direct deposit system for paying employees or contractors and make sure they receive their paystubs along with their payments.
This adds transparency to your payroll and provides employees with clear records of their earnings and deductions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Generating Paystubs
At this point, we know what a check stub generator is and how to use it. Are there mistakes in the process? Yes.
Below, we’ll talk about the common mistakes and how to avoid them.
Entering Incorrect Information
One of the biggest mistakes is inputting the wrong details—whether it’s the pay rate, hours worked, or tax deductions. A small error can throw off the entire paystub, leading to payroll issues.
Always double-check every detail before finalizing a paystub to ensure accuracy.
Forgetting to Include Deductions
Taxes, insurance, and other deductions are a key part of a paycheck. Skipping them can make the paystub look unrealistic or even non-compliant.
A reliable check stub generator automatically calculates deductions, but it’s still good to review them to ensure nothing is missing.
Not Saving Copies for Records
Once you generate a paystub, keeping a copy is important for tax filing and financial tracking. PaystubHero, allow you to store paystubs in your profile, making them easy to access later.
However, if your generator doesn’t offer storage, save them in a secure digital folder.
Using Unverified Paystub Generators
Not all paystub generators create accurate or legally compliant paystubs. Some may format them incorrectly, leaving out crucial details.
To avoid issues, always use a trusted platform that ensures professional, verifiable check stubs that meet legal standards.
How Long Should You Keep Your Paystubs?
While it may be tempting to toss them after checking your paycheck, holding onto them for the right amount of time can save you a lot of trouble down the road.
For Tax Purposes (At Least 3 Years)
The IRS recommends keeping financial records, including paystubs, for at least three years in case of an audit or tax review. Paystubs help verify your income and deductions, ensuring accuracy if any issues arise.
For Disputes or Errors (Up to 1 Year)
If there’s ever a payroll mistake like incorrect wages, missing deductions, or tax errors, you’ll need your paystubs as proof.
Keeping them for at least a year ensures you have records to resolve any disputes with your employer or tax agencies.
For Loan and Rental Applications (Until Approved)
When applying for a mortgage, car loan, or rental, lenders and landlords usually request recent paystubs.
Keep the last three to six months of paystubs handy until your application is processed and approved.
It’s a simple way to stay organized, make sure everything’s accurate.
For Long-Term Financial Records (Up to 7 Years)
If you want to be extra cautious, some financial experts suggest keeping paystubs for up to seven years along with other tax documents, especially if you’re self-employed or have complex tax situations.
To keep things organized, consider storing digital copies.
The Difference Between a
Paystub and a W-2
As we complete our guide on paystubs, a common question people normally ask is whether a paystub and a W-2 are the same. The answer?
Not quite.
Paystubs provide a detailed record of each paycheck, showing earnings, deductions, and taxes withheld.
A W-2, however, is an annual tax form that summarizes total earnings and tax withholdings for the entire year, which is necessary for filing taxes. While both matter, paystubs track finances regularly, while a W-2 is for tax reporting.